

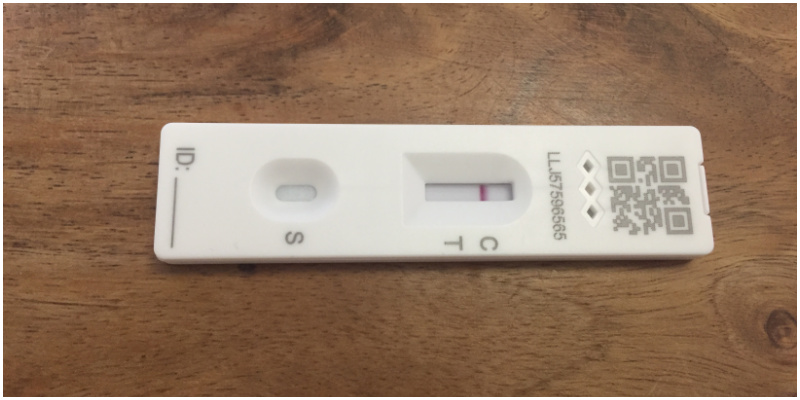
As shown in Figure 3, the sample is applied at one end of the strip, on the adsorbent sample pad, which is impregnated with buffer salts and surfactants that make the sample suitable for interaction with the detection system. A typical lateral flow test strip (presented in Figure 2) consists of overlapping membranes that are mounted on a backing card for better stability and handling. The principle behind the LFA is simple: a liquid sample (or its extract) containing the analyte of interest moves without the assistance of external forces (capillary action) through various zones of polymeric strips, on which molecules that can interact with the analyte are attached. Principle of the lateral flow immunoassay Nucleic acid LFA are used for the detection of amplicons which can be formed during the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). This review focuses on ‘lateral flow immunoassays’ (LFIAs), in which antibodies are exclusively used as recognition elements.
Moreover, because of the long shelf life and the fact that refrigeration is not required for their storage, LFA are very well adapted for use in developing countries, small ambulatory care settings, remote regions and battlefields.ĭepending on the elements of recognition used, LFAs can be categorized into different types ( Figure 1). This process has the potential to produce devices that may become powerful tools for new challenging applications such as early cancer detection. As the pathway for the development and introduction of novel technologies to the clinical diagnostics market requires hundreds of millions of dollars and decades of work, the improvement and further development of already established LFA technologies is a favourable alternative. LFAs are very good candidates as they are cheap to produce, easy to use and, importantly, widely accepted by users and regulatory authorities. Such assays (potentially a single LFA) should be easy to perform without the use of laboratory investigation, or individuals trained in chemical analysis. In recent years there has been an increasing demand for point-of-care multiple diagnostic assays with multiple test lines allowing the rapid and simultaneous detection of multiple analytes present in samples. In these areas of utilization, rapid tests are used to screen for animal diseases, pathogens, chemicals, toxins and water pollutants, among others. Further industries in which LFA-based tests are employed include veterinary medicine, quality control, product safety in food production, and environmental health and safety. A variety of biological samples can be tested using LFAs, including urine, saliva, sweat, serum, plasma, whole blood and other fluids. LFA-based tests are widely used in hospitals, physician's offices and clinical laboratories for the qualitative and quantitative detection of specific antigens and antibodies, as well as products of gene amplification. Low development costs and ease of production of LFAs have resulted in the expansion of its applications to multiple fields in which rapid tests are required.

The lateral flow assay (LFA) is a paper-based platform for the detection and quantification of analytes in complex mixtures, where the sample is placed on a test device and the results are displayed within 5–30 min.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
